 Click for a
larger image (12 Kb)
Click for a
larger image (12 Kb)
Paul Wiegert
Previously of the Dept. of Physics and Astronomy, York University, Toronto, Ontario, M3J 1P3 CANADA
Now at the The UWO Physics and Astronomy Dept ,
The University of Western Ontario, London,
Ontario CANADA.
Dept. of Physics and Astronomy, York University, Toronto, Ontario, M3J 1P3 CANADA
Seppo Mikkola
Tuorla Observatory, University of Turku, 21500 Piikkio FINLAND
The near-Earth asteroid 3753 Cruithne is now known to be a companion, and an unusual one, of the Earth. This asteroid shares the Earth's orbit, its motion "choreographed" in such a way as to remain stable and avoid colliding with our planet. This relationship was revealed in a paper by Paul Wiegert, Kim Innanen and Seppo Mikkola, and published in the British-based science journal Nature on June 12, 1997. A brief non-technical description of the motion of Cruithne is presented below. However, Cruithne's path is much more complicated than simple satellite motion; pondering the diagrams carefully should help clarify matters. Note: small images have been used to ensure fast downloading; click on any figure for a larger, clearer image.
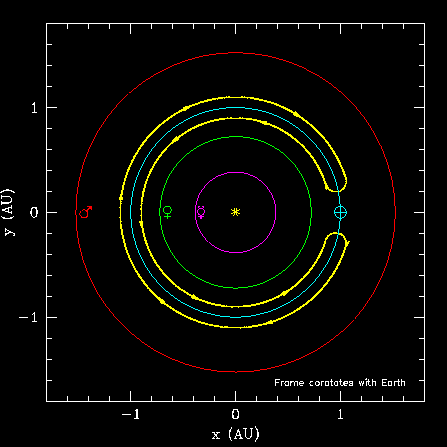
Before considering the motion of Cruithne, lets examine a less complicated situation first. The simplest type of horseshoe orbit is pictured below, for a hypothetical asteroid. Only the orbits of inner planets of the Solar System are shown. They are indicated by their traditional symbols: from the Sun outwards they are Mercury (magenta), Venus (green), Earth (blue) and Mars (red). The asteroid's path is shown in yellow.
 Click for a
larger image (12 Kb)
Click for a
larger image (12 Kb)
In this (co-rotating) picture, the Earth is stationary (at the crossed circle symbol), and we watch this hypothetical asteroid go around. We see it approach the Earth, and when it gets close enough, it turns around and retreats, only to repeat its performance on the other side. This unusual arrangement, in which close encounters with a planet do not result in impacts or strong distortion of the asteroids orbit is termed a "horseshoe" orbit because of its shape. Note that the asteroid doesn't go around the Earth, but rather shares the Earth's orbit with it.
 Another way to think of this horseshoe is to consider a three-lane,
circular race track. The Earth is a large truck moving at a constant
speed down the centre lane and the asteroid is a car. When in the
outer lane, the car is going a bit slower than the truck, and the
truck starts to catch up. But just when the truck is about to pass,
the car switches to the inner lane and speeds up. It then starts to
pull away from the truck, but because the track is circular, the car
will eventually catch up with the truck from behind. When it gets
close, the car again switches to the outer lane and slows down. Then
the whole cycle repeats. This is what is happening in a simple
horseshoe. Both vehicles share the same highway, but in a coordinated
fashion so as to avoid collision. In reality, the delicate
coordination of the asteroid and the Earth is performed by the laws of
celestial mechanics, and requires just the right conditions.
Another way to think of this horseshoe is to consider a three-lane,
circular race track. The Earth is a large truck moving at a constant
speed down the centre lane and the asteroid is a car. When in the
outer lane, the car is going a bit slower than the truck, and the
truck starts to catch up. But just when the truck is about to pass,
the car switches to the inner lane and speeds up. It then starts to
pull away from the truck, but because the track is circular, the car
will eventually catch up with the truck from behind. When it gets
close, the car again switches to the outer lane and slows down. Then
the whole cycle repeats. This is what is happening in a simple
horseshoe. Both vehicles share the same highway, but in a coordinated
fashion so as to avoid collision. In reality, the delicate
coordination of the asteroid and the Earth is performed by the laws of
celestial mechanics, and requires just the right conditions.
Horseshoes can be more complicated than that shown above. Though no examples have been known in nature before now, theoretical studies had shown that spiraling horseshoes, like that in the cartoon shown below, are also possible. In terms of the car-truck picture described above, the truck (the Earth) is still going at a constant speed in the centre lane, but the car is constantly changing lanes and speeds, so the truck sees it alternately fall back and pull forward. Though more complicated, the car still alternates between catching up with and falling behind the truck. Again, an asteroid in such an orbit would be effectively "repelled" from the Earth at each close approach (see the FAQ for more details)
 Click for a larger image (50 Kb)
Click for a larger image (50 Kb)
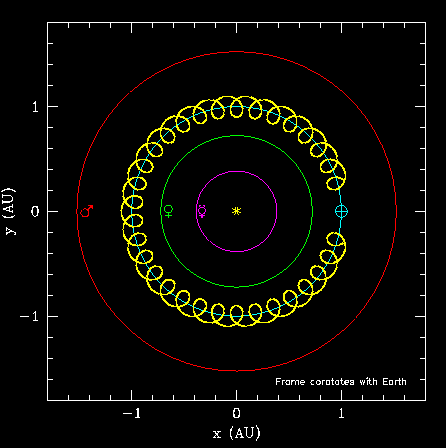
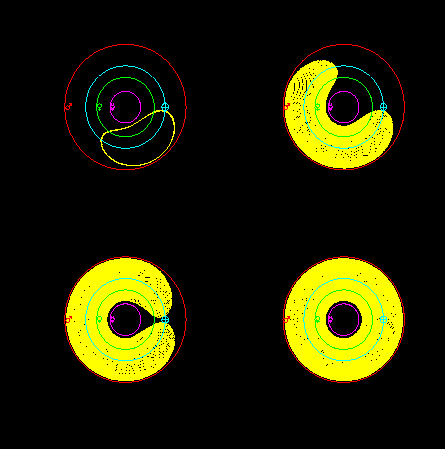
Cruithne is on an spiraling horseshoe orbit, similar to the one sketched above, but its behaviour is even stranger. First, it is an even more tightly-wound spiral, with kidney-bean shaped loops. Secondly, one part of the horseshoe actually overlaps the position of the Earth when viewed from above. A series of four frames (to be read left to right) showing a time lapse of Cruithne's horseshoe is shown below. Note again that Cruithne's horseshoe is composed of tightly wound kidney-bean shaped spirals which are almost impossible to distinguish individually in the picture. Remember, there are two types of motion going on: 1) every year, the asteroid traces out a kidney bean, 2) over time, this kidney bean drifts along the Earth's orbit, tracing out a spiral which, when complete (after 385 yrs) fills in an overlapping horseshoe".
 Click for a larger image (60 Kb)
Click for a larger image (60 Kb)
Though it appears (in the small image above) that a simple ring is formed, that is just a result of the asteroid's path overlapping the position of the Earth before reversing direction (Click on the picture to get a bigger and much clearer picture). The asteroid's tightly wound spiral horseshoe almost forms a complete ring before reversing direction, but a small gap does remain. This overlap is just another interesting and unexpected facet of the asteroid's behaviour, and is part of what makes this horseshoe the most complex known by far.
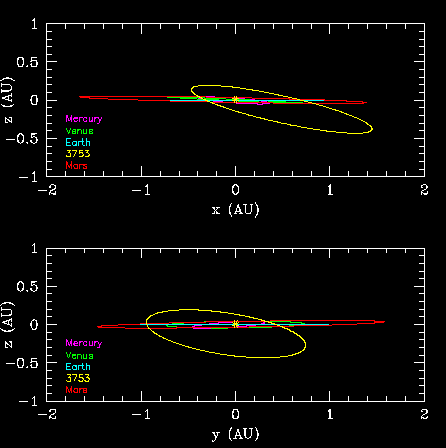
The apparent overlap of the asteroid with the Earth does not result in any danger of collision because the asteroid's orbit is highly inclined to that of our planet. The overlap is caused by the asteroid passing below the Earth's position. To illustrate this point, two edge-on views of the Solar System are shown below.
 Click for a larger image (25 Kb)
Click for a larger image (25 Kb)
 The high inclination of Cruithne's orbit relative to that of the other
planets is clear from these vantage points, and is what causes it to
avoid collisions. In fact, Cruithne doesn't even get particularly close to
the Earth: at its closest approach it only gets to within 0.1
astronomical units (about 15 million kilometers or 40 times the
Earth-Moon distance). The asteroid is currently just leaving the
"overlapping" portion of its horseshoe, and it will not get any closer
to us than 0.3 astronomical units (45 million km = 28 million miles)
in the near future. Each year, it is at its closest in the autumn and
at this point it will pass almost directly beneath the Earth's South
Pole!
The high inclination of Cruithne's orbit relative to that of the other
planets is clear from these vantage points, and is what causes it to
avoid collisions. In fact, Cruithne doesn't even get particularly close to
the Earth: at its closest approach it only gets to within 0.1
astronomical units (about 15 million kilometers or 40 times the
Earth-Moon distance). The asteroid is currently just leaving the
"overlapping" portion of its horseshoe, and it will not get any closer
to us than 0.3 astronomical units (45 million km = 28 million miles)
in the near future. Each year, it is at its closest in the autumn and
at this point it will pass almost directly beneath the Earth's South
Pole!
An image of Cruithne, taken by Sonia Keys with the 0.75 meter telescope at the Astronomical Society of Kansas City's Powell Observatory, is shown on the right. A wider view can be obtained by clicking on the image. Though relatively little is known about asteroid 3753 Cruithne, now that its most interesting aspects have been revealed, it will certainly become a focus of much more study. Perhaps Cruithne will be found to have more surprises yet.
As for the pronunciation....
The word is pronounced
"krooy-nyuh" which can also be written as "KROOee-nyuh" and in many other
ways. My point is that the stress is on the first syllable, which contains
both the OO and the ee sounds. The word has only two syllables, "cruith"
and "ne". The stress is not on the "ee" sound. The OOee or ooy (ui)
diphthong is very common in the Celtic languages.
Moran taing (many thanks) to DKC for the above guide to the pronunciation!
Note: It was the privilege of the discoverers of the asteroid, D. Waldron et al., to name their prize, a process which is regulated by the International Astronomical Union. For information see the FAQ or the IAU's Minor Planet Center naming conventions.
 PostScript file (350 Kb)
PostScript file (350 Kb)  PDF file (180 Kb)
PDF file (180 Kb)
 One
One
 Two
Two
 Three
Three
 Four
Four  Five
Five
 Six
Six
 Seven
Seven
 Eight
Eight
Standard:non-rotating frame
This animation shows the motions of the inner planets (Mercury, Venus,
Earth and Mars) and asteroid 3753 Cruithne over a few years. Note the highly
eccentric and inclined (camera will pan around to show this) orbit of
Cruithne, and the lack of obvious connection to the Earth, except that
they both go around the Sun in about the same amount of time. The
sizes of the planets are not to scale, but their orbits are.
From the non-rotating to the rotating frame
The relative motions of 3753 Cruithne and the Earth are shown. After a few
orbits, the lines of sight connecting Cruithne to the Earth are drawn in
green. Note that, though they both go around the Sun, both are always
on the same side of the Sun. Then, the Earth will begin "picking up" the
lines of sight, constructing the apparent path of Cruithne as seen from the
rotating Earth. Their motions are such that Cruithne appears to perform a
kidney-shaped loop around the Earth. Though the asteroid thus appears to
orbit the Earth, this is a result of the frame of reference we are using.
Also note that the presence of the Earth at the centre of the kidney is
simply a result of their mutual synchronization: the Earth is lined up with
the asteroid and Sun when the asteroid is at perihelion (its closest approach
to the Sun). If the Earth and asteroid are synchronized differently, the
asteroid will continue to perform a kidney-shaped loop every year, but the
loop will not be centred on the Earth. For example, if the Earth is 180
degrees away from Cruithne when the asteroid reaches perihelion, the kidney
bean will also be 180 degrees (ie. on the other side of the Sun) from our
planet.
The rotating frame
Because the asteroid and the Earth do not go around in exactly
the same amount of time (the asteroid currently goes around slightly
faster than the Earth), the position of the kidney-shaped loop
relative to the Earth varies over time. If the asteroid and the Earth
were not in a special arrangement, the Earth would face potential
danger as the asteroid drifted inexorably towards our planet. However,
in their current relationship, the kidney's direction of drift is
reversed every time it approaches the Earth. Through a remarkable
interaction of gravity and the laws of motion, the Earth's effectively "repels" the asteroid at each close approach!
MPEG movies
Note: Gravity does NOT become repulsive.
It is only the interplay between gravity and the physical laws of motion
which creates this effect. Consider a comet on a highly elliptical orbit around the Sun. At its closest approach, it doesn't plunge into the Sun
(unless it comes close enough to actually crash into it) but rather turns
around and heads back away from the Sun. Did the Sun's gravity become repulsive? Of course not, it is just that the velocity the comet gained
in falling towards the Sun is enough to carry it away again. The orbits
of comets (and Cruithne and all other Solar System bodies) are regulated
by this interplay between gravity and the laws of motion.
This movie demonstrates the drift of the kidney relative to the Earth, and how
it reverses direction upon
close approaches. Note that the asteroid passes beneath the Earth at
times. The drift rate of the asteroid has been increased by a factor
of about 40 for ease of display: there are really about 40
kidney-loops for every one shown.
Related links
Have a question or comment? Email Paul Wiegert at pwiegert[remove this and put the @ symbol here]uwo.ca
Note that this page is not actively maintained: some information may be out of date.
Near-Earth asteroid 3753 Cruithne main page
© Copyright 1997-2020 by Paul Wiegert